- Reaction score
- 9,514
- Points
- 1,160
83,303 convertible CRV-7 rounds currently being divested.
Guided version[edit]
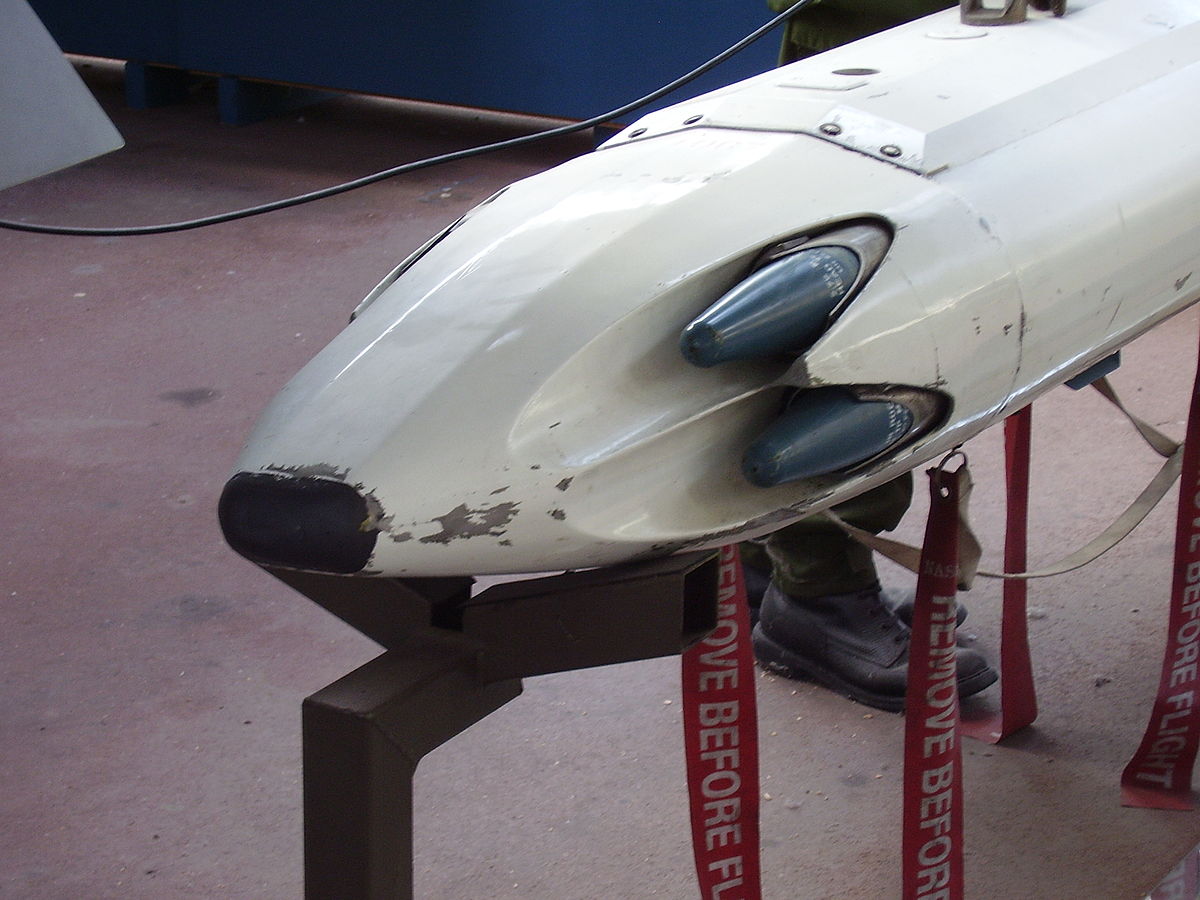
In 2006 Bristol started testing a new version of the CRV7, the CRV7-PG. The weapon was introduced at Eurosatory 2006.[16] Bristol's current owners, Magellan Aerospace, offered it for sale starting in 2007.
The PG version, for "precision guided", adds a seeker developed by Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace to the front of any version of an otherwise unmodified CRV7. The seeker uses a simple inertial guidance system through the midcourse, and homes during the terminal approach using a laser designator. Other versions offer anti-radiation seeking, or GPS guidance. The precision guided kit includes the addition of tail fins and an in-flight control system. Combining the laser seeker with the FAT warhead produces a capable long-range anti-tank missile that is faster and much less expensive than traditional platforms like the AGM-114 Hellfire.
A version of the CRV7-PG was also developed for special forces use, fired from a single tube mounted on a 6 x 6. In use, the weapon would be driven into the field and fired from behind cover, aiming at a designated location from a forward team.[17]
- Milan Machala & Radek Doskocil , "Contemporary Trends in Development and Modernization of Rocket Systems" Archived 2011-07-21 at the Wayback Machine

CRV7 - Wikipedia
 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
And of course there is a Canadian carriage prototyped and tested.
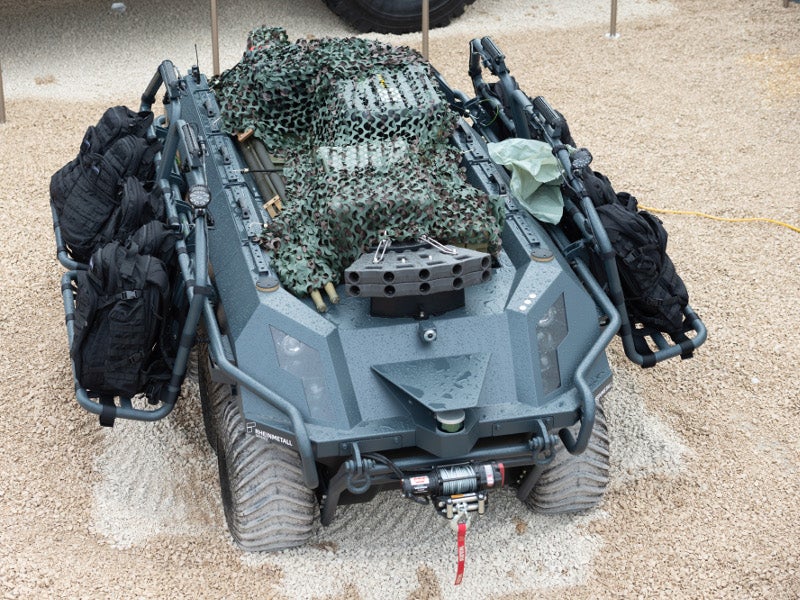


Mission Master Unmanned Ground Vehicle, Germany
The Mission Master unmanned ground vehicle is produced by Rheinmetall to support multiple mission requirements of troops in difficult terrain conditions.
The vehicle has a length of 2.95m and a base weight of approximately 750kg. Its modular design allows for carriage of 600kg easy-to-install payloads for operations on land, while its payload carrying capacity is reduced to 300kg during amphibious operations.
LG1 has a mass of 1520 kg without ammunition
C3 has a mass of 2400 kg without ammunition
And Arnold also produces this 23 round package

| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Production history | |
| Service history | |
| AGR-20 (APKWS II) | |
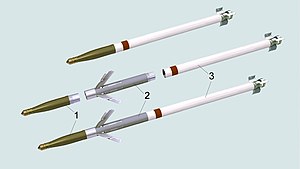 1)top picture: standard Hydra-70 2)bottom picture: APKWS | |
| Type | Rocket |
| Place of origin | United States |
| In service | 2012-present |
| Used by | See Future and potential users |
| Manufacturer | BAE Systems |
| Unit cost | $22,000[1] |
| No. built | 50,000[2] |
| Mass | 32 lb (15 kg)[3] |
| Length | 73.8 in (1.87 m)[3] |
| Diameter | 2.75 in (70 mm) (unfired)[4] |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,000 m/s (3,600 km/h; 2,200 mph; Mach 2.9) at max[4] |
| Effective firing range | 1,100–5,000 m (0.68–3.11 mi) (rotary wing); 2–11 km (1.2–6.8 mi) (fixed wing)[5][3] |
| Maximum speed | 2,425 ft/s (739 m/s)[6] |
| Guidance system | Distributed Aperture Semi-Active Laser Seeker |
| Launch platform | See Launch platforms |
The AGR-20 Advanced Precision Kill Weapon System (APKWS) is a design conversion of Hydra 70 unguided rockets with a laser guidance kit to turn them into precision-guided munitions (PGMs).[7] APKWS is approximately one-third the cost and one-third the weight of the current inventory of laser-guided weapons, has a lower yield more suitable for avoiding collateral damage, and takes one quarter of the time for ordnance personnel to load and unload.










